Service hotline
+86 0755-83044319
release time:2024-06-26Author source:SlkorBrowse:18511

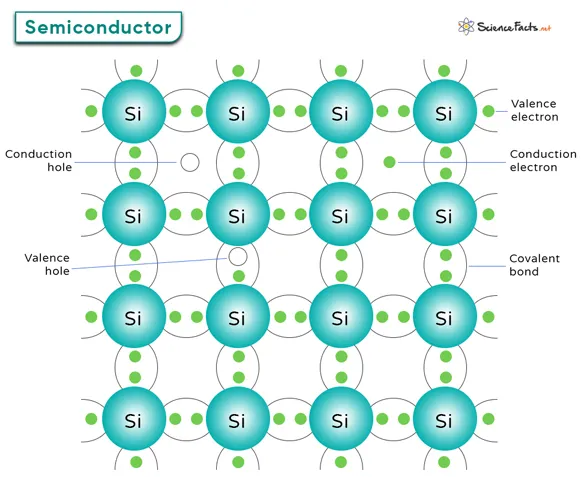


l Silicon minerals are used as structural compounds,such as clay, silica sand, building mortar, plaster, and building stones.
l Silicon minerals are also employed in the production of concrete.
l Silicon dioxide is used to manufacture refractory bricks for furnace linings.
l It is utilized in the production of white ceramics like soda-lime glass and porcelain.
l Silicon dioxide is essential in making optical fibers, which are widely used in telecommunications and computer networks.
l It is used to produce fiberglass and glass wool, which are crucial for structural support and insulation.
l Silicon is used to manufacture mechanical seals and waterproof materials.
l Wax and high-temperature lubricants are made from silicon.
l For medical purposes, silicon is used in breast implants and contact lenses.
l Silicon is used to make high-temperature alloys.
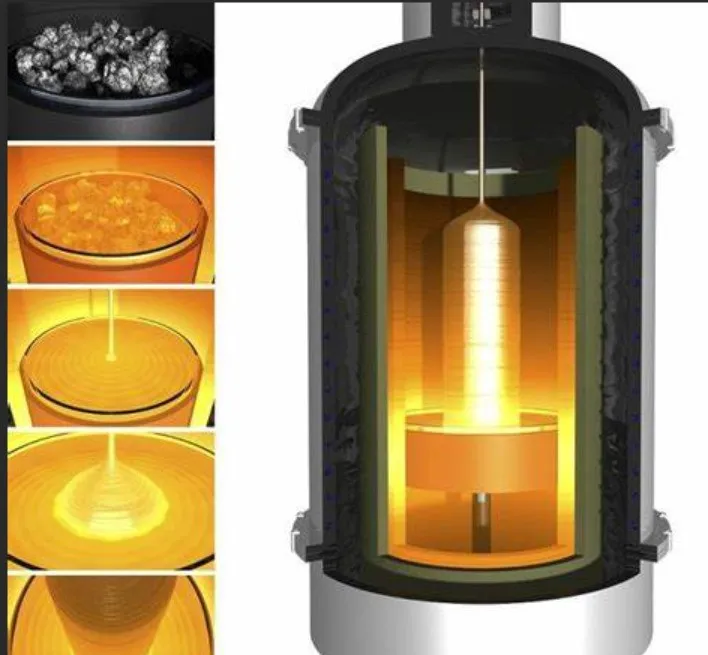
l Silicon is essential for producing silicon wafers, which have extensive applications in the semiconductor industry.
l Silicon is also vital for human health; the density of human skin, nails, hair, and bones depends on the silicon content.
l Silicone resins are synthetic polymers produced from silicon.
l Solar cells, semiconductor detectors, transistors, and other semiconductor devices used in the computer industry are all made from silicon.
l Silicon is a crucial component of integrated circuits (ICs), which are fundamental to our electronic devices, such as computers and mobile phones.
l Free silicon is used in the cast aluminum and steel refining industries.









Site Map | 萨科微 | 金航标 | Slkor | Kinghelm
RU | FR | DE | IT | ES | PT | JA | KO | AR | TR | TH | MS | VI | MG | FA | ZH-TW | HR | BG | SD| GD | SN | SM | PS | LB | KY | KU | HAW | CO | AM | UZ | TG | SU | ST | ML | KK | NY | ZU | YO | TE | TA | SO| PA| NE | MN | MI | LA | LO | KM | KN
| JW | IG | HMN | HA | EO | CEB | BS | BN | UR | HT | KA | EU | AZ | HY | YI |MK | IS | BE | CY | GA | SW | SV | AF | FA | TR | TH | MT | HU | GL | ET | NL | DA | CS | FI | EL | HI | NO | PL | RO | CA | TL | IW | LV | ID | LT | SR | SQ | SL | UK
Copyright ©2015-2025 Shenzhen Slkor Micro Semicon Co., Ltd