Service hotline
+86 0755-83044319
release time:2025-03-18Author source:SlkorBrowse:2791
This article introduces the working principles of microphone sensors and their wide-ranging applications in modern technology. Microphones convert acoustic energy into electrical energy through diaphragm vibrations, utilizing transduction mechanisms such as electromagnetic, capacitive, MEMS, or piezoelectric methods to achieve signal conversion. The output signal is optimized through pre-amplification and signal conditioning. 
Microphone sensors are essential components that enable us to capture sound and convert it into electrical signals, playing a critical role in modern technology. From simple voice recording to complex audio processing, these sensors transform acoustic energy into electrical energy, making them applicable in communication systems, entertainment, and industrial environments. Different types of microphone sensors operate on varying principles and are optimized for specific uses. Understanding how these sensors work and their respective advantages is crucial for selecting the right microphone for a given application.
At their core, microphone sensors are transducers: devices that convert energy from one form to another. In this case, the energy conversion is from acoustic energy (sound waves) to electrical energy (voltage). When sound waves strike the microphone's diaphragm, they cause it to vibrate. These vibrations are then converted into electrical signals that reflect the amplitude and frequency of the sound waves.
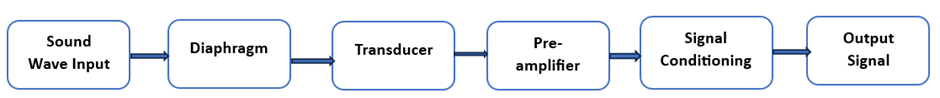
● Sound Wave Input: Incoming sound waves from the environment.
● Diaphragm: The diaphragm responds to sound waves and generates vibrations, producing mechanical motion.
● Transduction Mechanism (Transducer): Converts mechanical vibrations into electrical signals.
★ Electromagnetic (dynamic microphones)
★ Capacitive (condenser microphones)
★ MEMS-based (MEMS microphones)
★ Piezoelectric (piezoelectric microphones)
● Pre-amplifier: Amplifies the weak electrical signal generated by the transduction mechanism.
● Signal Conditioning: May include filtering, equalization, or noise reduction to optimize signal quality.
● Output Signal: The processed electrical signal is output to recording, processing, or transmission systems.









Site Map | 萨科微 | 金航标 | Slkor | Kinghelm
RU | FR | DE | IT | ES | PT | JA | KO | AR | TR | TH | MS | VI | MG | FA | ZH-TW | HR | BG | SD| GD | SN | SM | PS | LB | KY | KU | HAW | CO | AM | UZ | TG | SU | ST | ML | KK | NY | ZU | YO | TE | TA | SO| PA| NE | MN | MI | LA | LO | KM | KN
| JW | IG | HMN | HA | EO | CEB | BS | BN | UR | HT | KA | EU | AZ | HY | YI |MK | IS | BE | CY | GA | SW | SV | AF | FA | TR | TH | MT | HU | GL | ET | NL | DA | CS | FI | EL | HI | NO | PL | RO | CA | TL | IW | LV | ID | LT | SR | SQ | SL | UK
Copyright ©2015-2025 Shenzhen Slkor Micro Semicon Co., Ltd